Brown Rice vs White Rice

- In the realm of nutrition, the debate between brown rice and white rice has been ongoing.
- While some tout the nutritional superiority of brown rice, others argue in favor of white rice, emphasizing its convenience.
- In this comprehensive analysis, we delve into the scientific evidence surrounding both types of rice to help readers make informed dietary choices.
Understanding the Nutritional Composition:
A. Brown Rice:
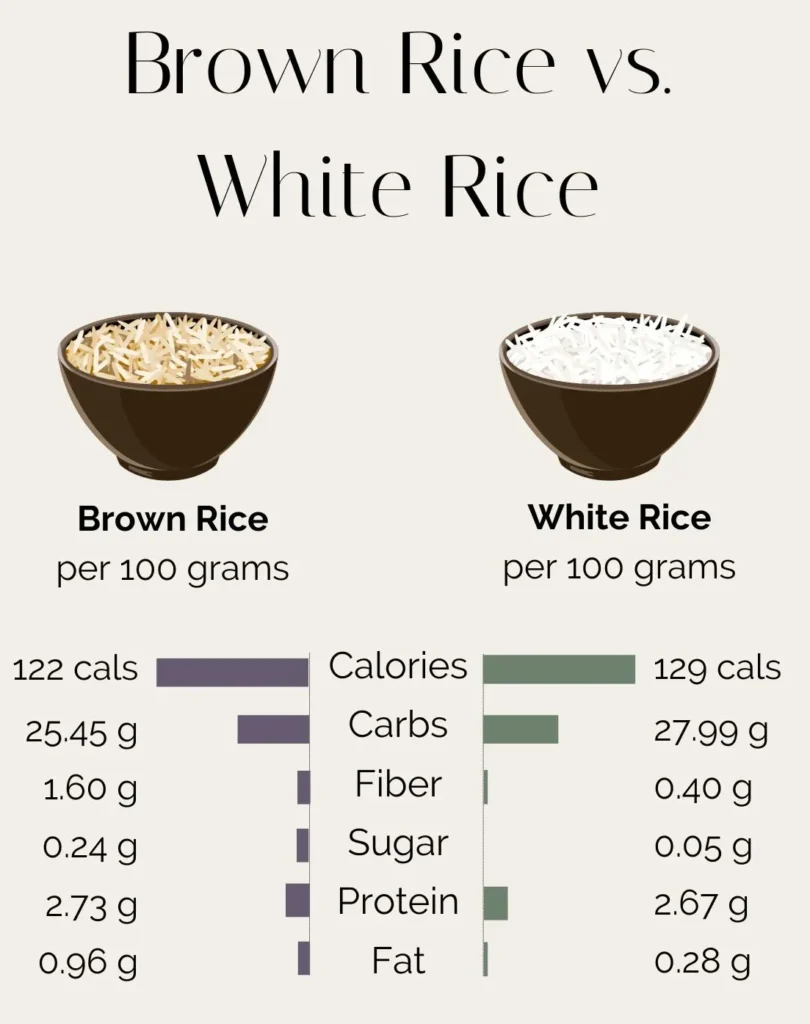
- Rich in fiber, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals.
- Contains the fibrous bran and nutritious germ, providing comprehensive nutrition.
- Fiber content aids in digestion, regulates blood sugar levels, and promotes heart health.
B. White Rice:
- Lacks the fibrous bran and nutritious germ due to processing.
- Often enriched with B vitamins and iron, albeit to a lesser extent compared to brown rice.
- Provides quick energy but lacks the sustained satiety offered by brown rice due to lower fiber content.
Health Benefits and Drawbacks:
A. Brown Rice:
Benefits:
- i. Regulation of blood sugar levels, making it suitable for diabetes management.
- ii. Promotion of weight management through increased satiety and reduced calorie intake.
- iii. Contribution to overall health with its rich nutrient profile.
Drawbacks:
- i. Presence of phytic acid and higher levels of arsenic, potentially affecting mineral absorption and posing health risks if consumed excessively.
- ii. Possibility of digestive discomfort, especially for individuals transitioning to a high-fiber diet.
- iii. Shorter shelf life compared to white rice due to higher fat content in the germ.
B. White Rice:
Benefits:
- i. Convenient source of quick energy, suitable for individuals with high energy requirements.
- ii. Enriched with essential nutrients, albeit not as comprehensive as brown rice.
Drawbacks:
- i. Lack of fiber and some nutrients found in brown rice, leading to quicker digestion and potential blood sugar fluctuations.
- ii. Reduced satiety compared to brown rice, which may result in overeating.
- iii. Limited contribution to overall health due to lower nutrient density compared to brown rice.
Considerations for Specific Dietary Goals:
A. Blood Sugar Management:
- Brown rice’s higher fiber content aids in stabilizing blood sugar levels, making it preferable for individuals with diabetes or prediabetes.
b. Weight Management:
- Brown rice’s fiber content promotes satiety, helping individuals control calorie intake and manage weight effectively.
c. Overall Health:
- Incorporating brown rice into a balanced diet provides a more comprehensive array of nutrients, supporting heart health, weight control, and overall well-being.
Addressing Common Misconceptions:
A. Myth: Brown rice is always healthier than white rice.
- Reality: While brown rice offers superior nutritional benefits, both types of rice can be part of a healthy diet depending on individual preferences and dietary goals.
B. Myth: White rice is devoid of nutrients.
- Reality: Enriched white rice still provides essential nutrients, albeit in lower quantities compared to brown rice, making it a viable option for certain dietary needs.
C. Myth: Brown rice is the only option for managing blood sugar levels.
- Reality: While brown rice is beneficial for blood sugar management, portion control and overall dietary balance are equally important factors.
Practical Considerations:
A. Availability and Cost:
Brown rice may be more expensive and less readily available in some regions compared to white rice.
B. Culinary Preferences:
- Taste and texture preferences may influence individuals’ choice between brown and white rice.
C. Storage and Shelf Life:
- Brown rice’s shorter shelf life due to its higher fat content requires proper storage to prevent spoilage, whereas white rice tends to have a longer shelf life.
- Both brown rice and white rice have their respective benefits and drawbacks.
- Understanding individual dietary needs and preferences is crucial in making informed choices between the two.
- Incorporating a variety of whole grains, including brown rice, into a balanced diet ensures optimal nutrition and promotes overall health and well-being.
for more health tips clickhere
